What is a Standard?
A Standard is a guideline approved by a recognised body that provides for common and repeated use, rules, guidelines or characteristics for products, processes and production methods, with which compliance is not mandatory.
Types of Standards:
Standards can be of many types; the more common types are:
- Testing standards;
- Product standards;
- Process standards;
- Service standards; and
- Management systems standards.
Who Benefits from Standards?
Standards provide technological, economic and societal benefits:
- Businesses can offer products that meet international specifications and therefore gain market access.
- Consumers are afforded a wider choice of safe, reliable and consistent quality products.
- Governments have the scientific and technological basis for health, safety and environmental legislation.
- Trade officials can use standards to level the playing field and arbitrate trade disputes.
- For developing countries, standards represent internationally recognised best practices and could be an important source of technological know-how. Standards provide a basis a basis for making correct decisions when investing scarce resources.
- For everyone, standards improve the quality of life.
Standards Development Process:
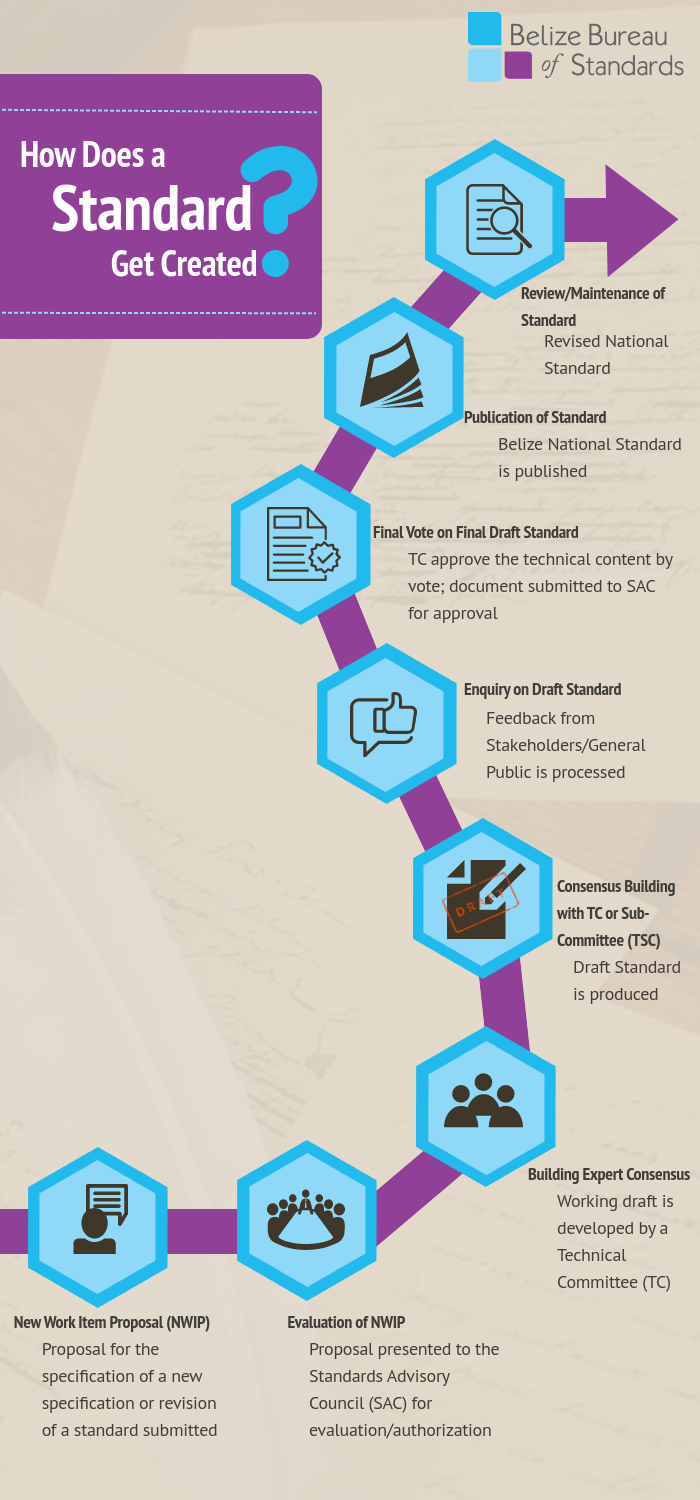
| Stage 00 — Preliminary | Request received, evaluation conducted and project submitted for authorization. |
| Stage 10 — Proposal | The proposal is presented to the Standards Advisory Council (SAC) for evaluation/authorization and if recommended for establishment of standard then a Technical Committee (TC) or Sub-Committee is formed or the project is assigned to an existing TC. |
| Stage 20 — Preparatory | Working draft is developed along with the TC and a project schedule is established; This involves the collection of technical and trade data to develop working draft. |
| Stage 30 — Committee | Principal stage at which comments from members of the committee are taken into consideration, with a view to reaching consensus on the technical content of the standard and usually involves a number of committee meetings. |
| Stage 40 — Enquiry | The enquiry stage (draft for public comment) is the principal stage at which comments from the general public and stakeholders are taken into consideration; Advertisement of the standard for public comments giving a minimum of 60 days to comment on draft standards. If substantial comments received, then draft is amended; TC reaches consensus on draft, TC conducts a quality review and a pre-approval edit is completed. |
|
Stage 50 — Approval |
The TC approves the technical content of the draft document by vote and a second level review is conducted to verify that standards development procedures were followed; The document is submitted to the SAC for approval and recommendation to be established as a standard. |
| Stage 60 — Publication | Final edit is conducted to verify conformity with the applicable editorial and procedural requirements; At this stage it is recommended that a marketing awareness plan be established to let everyone know that a new  standard is available |
| Stage 90 — Review | This stage a systematic, periodic review of the standard is performed in an effort to keep it current and technically valid, if found adequate is only a need to confirm the standard and state this in the standards catalogue; May include publication of amendments, the interpretation of a standard or clause. The systematic review of all standards occurs every three years. |



